Macro Allocation Strategy
This strategy targets portfolio diversification and overall return potential through tactical asset allocation.
Welcome to Invesco’s Global Systematic Investing Study 2024. This year’s study continues to provide valuable insights into the rapidly evolving landscape of systematic investing, chronicling the latest innovations and how practitioners globally are leveraging advanced quantitative techniques across asset classes.
Welcome to the ninth iteration of Invesco's Global Systematic Investing study. The study continues to focus on the usage of systematic investing across the industry, with over 140 practitioners surveyed collectively managing more than 23 trillion in assets. This year's themes include applications and multi-asset portfolios, the evolution of multifactor strategies, the impact and use of artificial intelligence. And finally, how systematic investing is used to develop highly customized ESG strategies.
The first theme explores the rise of systematic strategies and multi-asset portfolio construction, with the acceptance of factors across more asset classes like equities and fixed income. Investors have now embraced systematic strategies in the construction of more resilient multi-asset portfolios. An adaptive and data driven approach now allows investors to use these strategies to navigate a wider investment universe and more complex macro environment.
In the second theme, the study explores how multifactor strategies have become more mainstream as investors seek and more precise way to capture the broader spectrum of return opportunities. The study also seeks to understand how investors are addressing concerns around equity market concentration through a more diversified approach and factor allocations.
In the third theme, we continue to explore the rise of artificial intelligence in the investment process while AI usage has increased year over year. This hasn't come without challenges. Respondents identified data availability and quality as a concern alongside regulatory and governance considerations. In addition, investors continue to evaluate the economic rationale of any new factor or signal that are generated by these new techniques.
In the fourth and final theme, the study continues to explore the relationship between systematic investing and ESG implementation. The study has found systematic approaches have become increasingly popular due to their ability to offer more scalable customization.
thank you for your interest in this year's report.
We hope you enjoyed these valuable insights and look forward to engaging with you on this year's study.
Based on interviews with 131 systematic investors — defined as investors that employ structured, rules-based quantitative models and algorithms to make investment decisions — this research collects the opinions of senior decision-makers responsible for managing $22.3 trillion in assets (as of March 31, 2024).
Time to watch: 3:33
The research identified four main themes: The embracement of systematic strategies to construct multi-asset portfolios, the evolution of multi-factor strategies into a standard approach, the expanding role of artificial intelligence (AI) in investment processes, and the increasing demand for customized solutions to meet investors’ sustainability objectives.
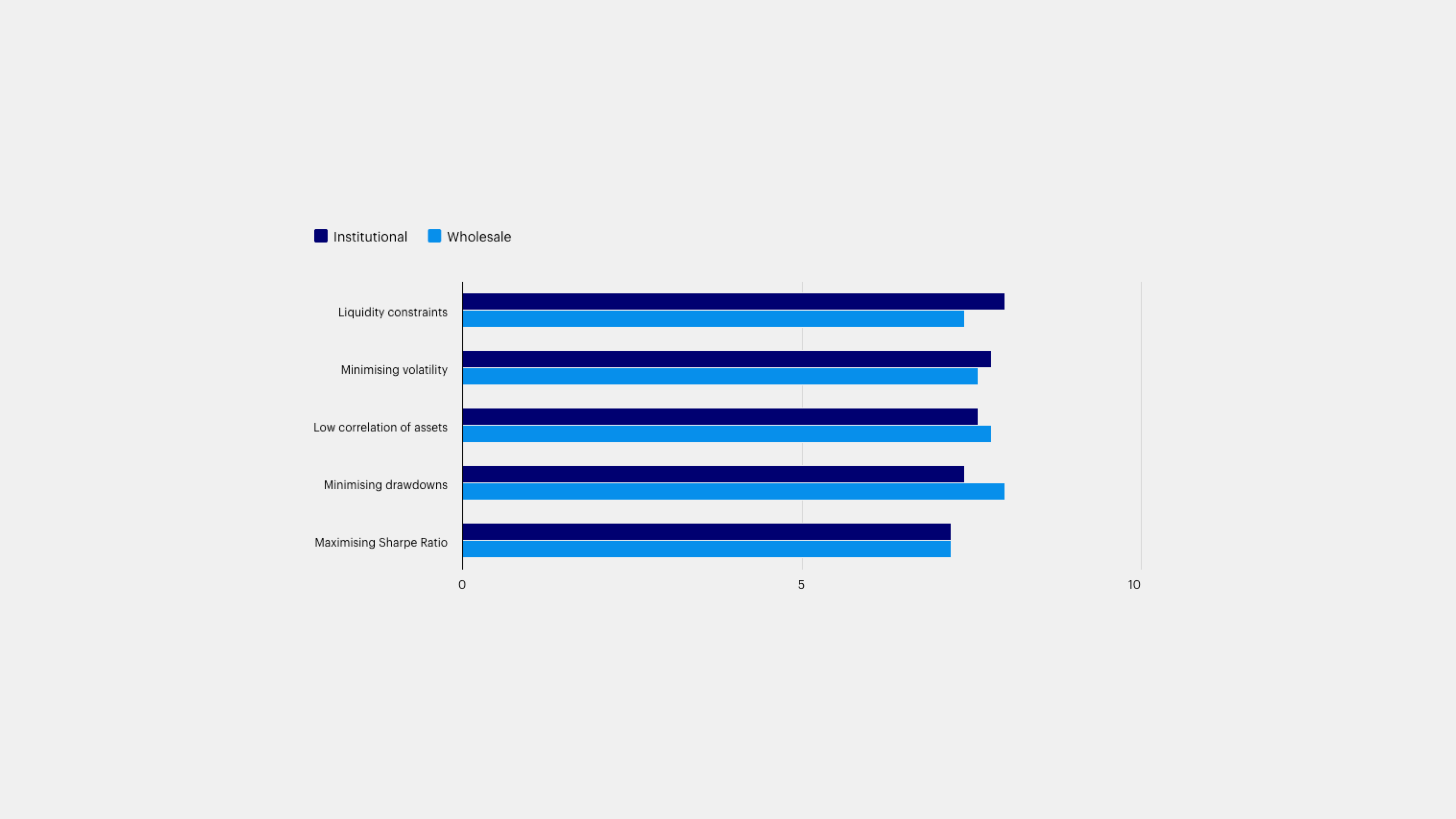
Institutional and wholesale investors consider varying factors when constructing multi-asset portfolios, such as maintaining liquidity and minimizing volatility.
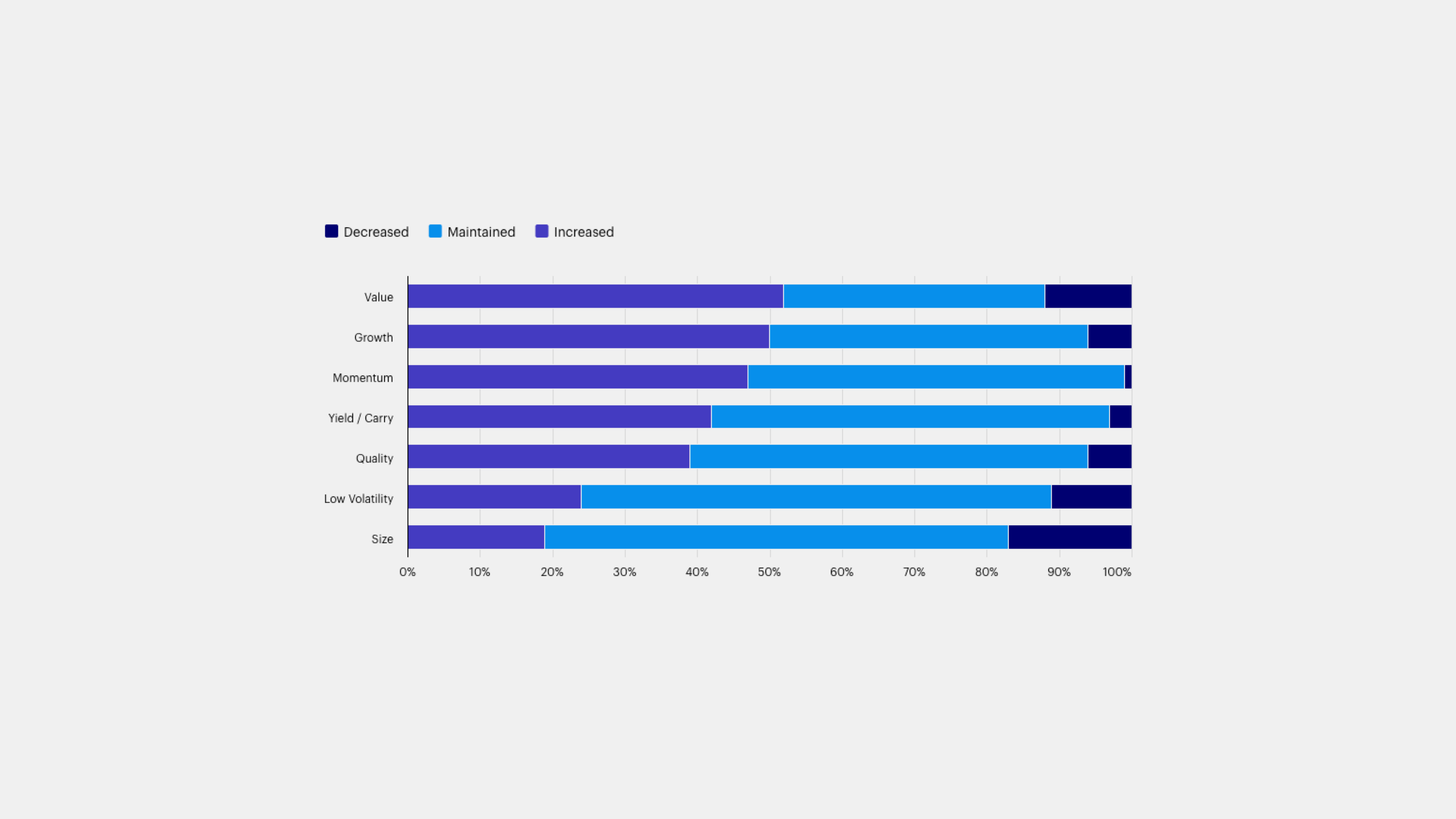
The second theme explores the evolving dynamics of multi-factor investing, which is now the norm as factor returns create opportunities and challenges for investors.
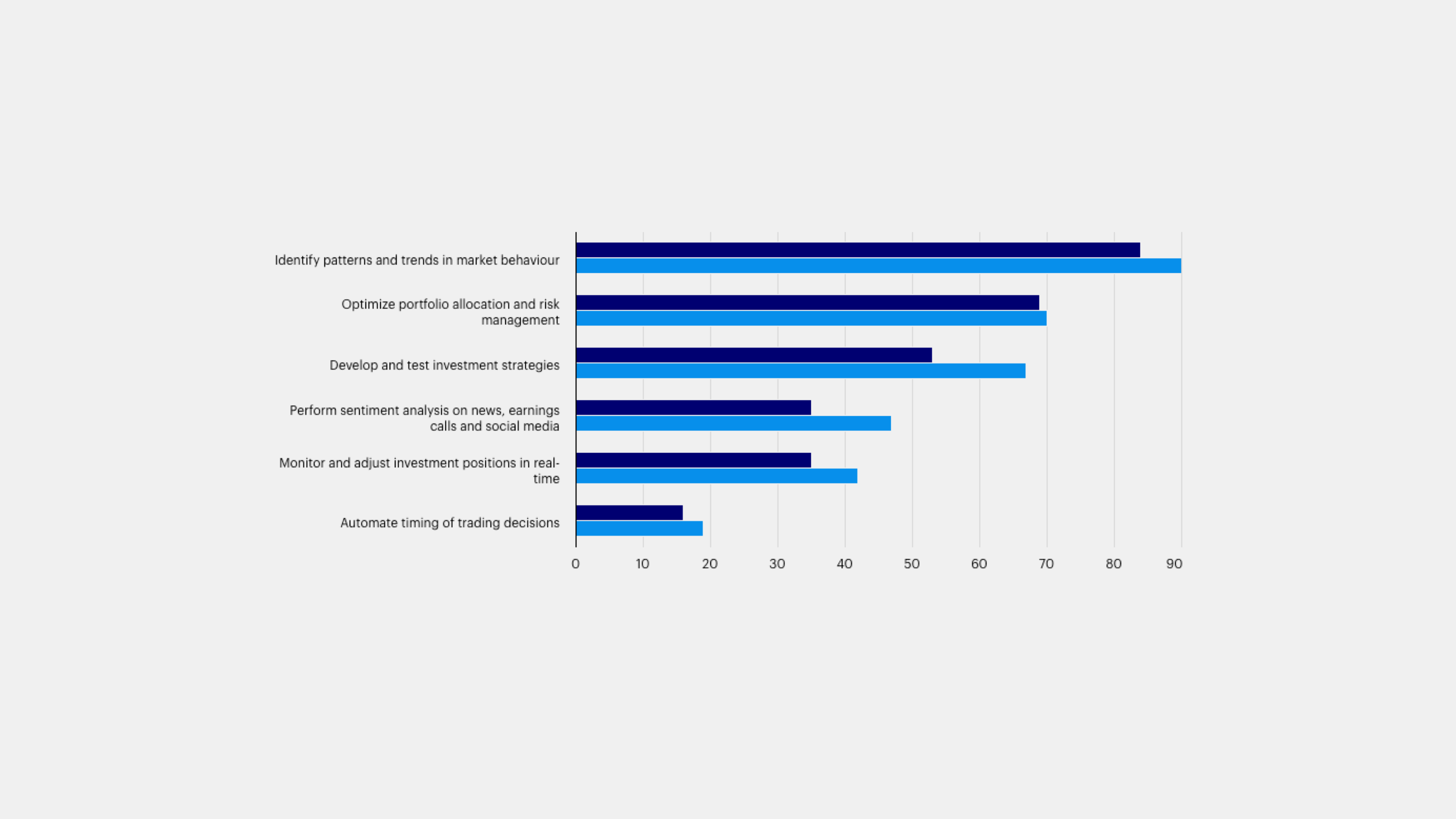
AI’s transformation from investors using it as a peripheral tool to applying it to their investment processes, such as for portfolio optimization, is the focus of the third theme.
The fourth theme explores a shift toward investors employing a systematic approach to integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into their portfolios.
By focusing on the future landscape, this research offers timely perspectives on how investors are deploying (and looking to deploy) advanced methodologies to construct resilient portfolios and potentially generate alpha.
Harness the power of diversified factor strategies for better portfolio resilience through any market conditions

Macro Allocation Strategy
This strategy targets portfolio diversification and overall return potential through tactical asset allocation.

Dynamic Multifactor
Discover our rotational strategy that seeks to anticipate changes in the business cycle and tilt toward factors expected to outperform in each market regime.

Custom Portfolio Solutions
We combine an outcomes-based focus with tailored investment solutions to deliver custom portfolios and analysis.

ETFs for institutions
Explore the breadth of our ETF capabilities and our expansive platform with experts dedicated to supporting your investment goals.
The value of investments and any income will fluctuate (this may partly be the result of exchange rate fluctuations), and investors may not get back the full amount invested.
Factor investing (as known as smart beta or active quant) is an investment strategy in which securities are chosen based on certain characteristics and attributes that may explain differences in returns. Factor investing represents an alternative and selection index based methodology that seeks to outperform a benchmark or reduce portfolio risk, both in active or passive vehicles. There can be no assurance that performance will be enhanced or risk will be reduced for strategies that seek to provide exposure to certain factors. Exposure to such investment factors may detract from performance in some market environments, perhaps for extended periods. Factor investing may underperform cap-weighted benchmarks and increase portfolio risk. There is no assurance that the investment strategies discussed in this material will achieve their investment objectives.


Let us know using this form and one of our specialist team will quickly get back to you.
Institutional and wholesale investors consider varying factors when constructing multi-asset portfolios, such as maintaining liquidity and minimizing volatility. These factors align closely with the capabilities of systematic strategies, which offer investors a powerful tool for achieving their investment objectives. As one North American institutional investor noted, “We’re moving beyond static allocations to a more dynamic, data-driven approach that can better navigate volatility and capture opportunities across asset classes.”
Rate the following factors in order of importance for multi-asset portfolio construction: (Score 1-10 where 10 is very important). Grouped by Investor Institutional/Wholesale, chart shows the factors used by respondents to construct multi-asset portfolios. Liquidity constraints: 8.0/7.4, Minimizing volatility: 7.8/7.6, Low correlation of assets: 7.6/7.8, Minimizing drawdowns: 7.4/8.0, Maximizing Sharpe ratio: 7.2/7.2.
The second theme explores the evolving dynamics of multi-factor investing, which is now the norm as factor returns create opportunities and challenges for investors. For example, as mega-cap tech stock dominance increased concentration risk, investors have sought solutions through factor investing — including an increase in allocations to Value as a potential hedge.
Over the last 12 months, have you increased, decreased, or maintained your allocations to these factors (ignoring market impacts)?
AI’s transformation from investors using it as a peripheral tool to applying it to their investment processes, such as for portfolio optimization, is the focus of the third theme. AI applications in investment are diverse and expanding, and emerging applications are gaining traction rapidly. For instance, 47% of investors use AI for sentiment analysis of news, earnings calls, and social media, up from 35% in 2023. This real-time gauge of market sentiment offers a potential edge in fast-moving markets.
How do you use AI in your investment process? Grouped by 2023/2024, chart shows how AI is used in the investment process by respondents. Identify patterns and trends in market behavior: 84/90, Optimize portfolio allocation and risk management: 69/70, Develop and test investment strategies: 53/67, Perform sentiment analysis on news, earnings calls and social media: 35/47, Monitor and adjust investment positions in real time: 35/42, Automate timing of trading decisions: 16/19.
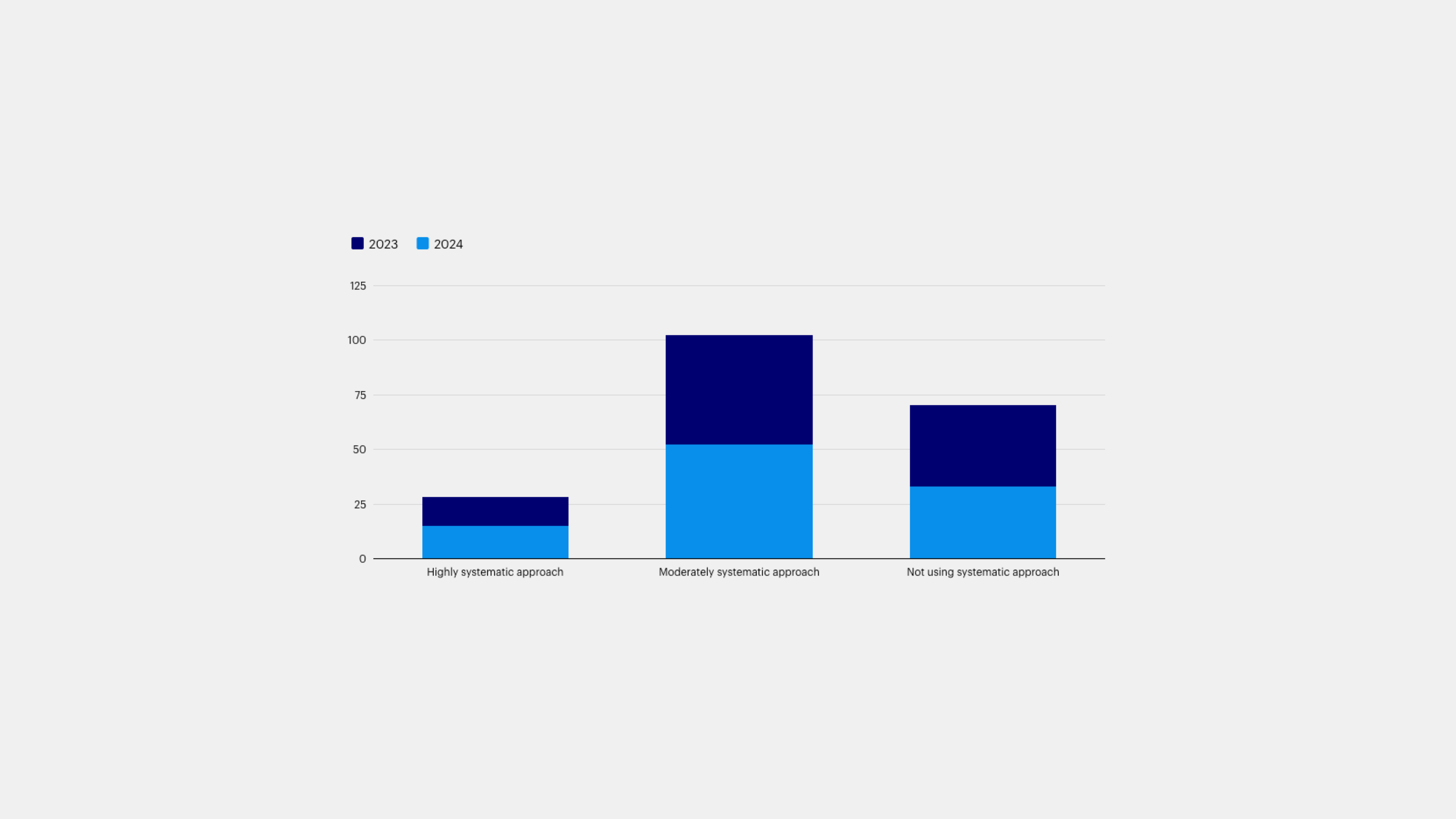
The fourth theme explores a shift toward investors employing a systematic approach to integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into their portfolios. According to one institutional investor from Europe, “Off-the-shelf ESG solutions no longer suffice. We need the ability to fine-tune our ESG approach to reflect our specific priorities and the unique ESG challenges in our investment universe. Systematic strategies give us the tools to do that.”
To what extent are you using a systematic approach to implement ESG? Divided by 2023/2024, chart shows to what extent respondents are using a systematic approach to implement ESG. Not using systematic approach: 37/33, Moderately systematic approach: 50/52, Highly systematic approach: 13/15.
While factor investing has historically been the cornerstone of systematic strategies, investors today are broadening their toolkits and using more diverse strategies (figure 1). As one North American wholesale investor noted: “Traditionally, factor investing has been based around overweighting specific factors, such as value and momentum, to capture risk premia. Systematic investing now encompasses a broader range of quantitative methodologies.”
Which of the following systematic methodologies/tools are you using in your portfolio construction? Sample size: 130. Grouped by Region Total/APAC/EMEA/North America showing the responses for the tools and methodologies used by respondents. Factor based investing: 94/93/94/94, Dynamic asset allocation: 78/77/73/82, Multi-asset analytics: 51/50/35/67, Systematic risk mitigation using derivatives/options: 51/60/41/55, Quantitative ESG models: 43/63/35/39, Machine learning/AI: 30/50/12/35.
The second theme explores the evolving dynamics of systematic investing. This study has highlighted the trend towards a more dynamic approach to adjusting factor exposure over the past several years. We find that nearly three-quarters of respondents adjust through time (figure 2), utilizing a broad range of tools to target specific factors at any point. Additionally, this year’s study has found nearly 80% of respondents view ‘growth’ as an additional factor.
Do you adjust your factor weights through time? Sample size: 130. Chart shows by region responses to whether respondents adjust factor weights through time no/yes. Total: 25/75, APAC: 27/73, EMEA: 14/86, North America: 33/67.
Data and technology become the focus of the third theme. The rise of AI has been noticed by systematic investors, with almost 50% of respondents already implementing some form of AI (figure 3). Adoption is expected to continue and expand across systematic investing practitioners.
Do you incorporate AI into your investment process? Sample size: 130. Divided by Retail and Wholesale respondents, chart shows the responses split for Use of AI in the investment process for AI used extensively/AI used to a limited extent/Do not use AI but considering/Do not use AI and not considering. Institutional: 10/35/44/11, Wholesale: 8/42/40/10.
The fourth and final theme for 2023 continues the exploration of systematic investing’s intersection with environmental, social and governance (ESG) investing. Two-thirds of respondents reported using systematic tools in their ESG investing, citing improved performance and risk management as the key drivers (figure 4). The rise of technology from the third theme continues to the fourth, with half of respondents expecting to increase their use of AI and other systematic tools to reconcile data inconsistencies and analyze large data sets more effectively.
What are the advantages of a systematic approach to applying ESG? Sample size: 100. Chart showing the advantages of systematic approach to ESG split by Total/APAC/EMEA/North America. Improved performance: 77/90/50/89, Improved risk management: 71/83/69/63, Enhanced portfolio diversification: 59/67/53/58, Increased efficiency/lower costs: 39/43/44/32, Improved scalability and capacity: 36/37/34/37, Identification and control of portfolio tilts/bias: 29/23/41/24.
NA3266344