UNDERSTAND DIFFERENT TYPES OF INVESTMENTS

Investment Education
Different Types of Investments
Different Types of Investments
Understand Different Types of Investments
Stocks
- An investor purchasing a company’s shares effectively owns part of the company.
- A shareholder may be able to get dividends.
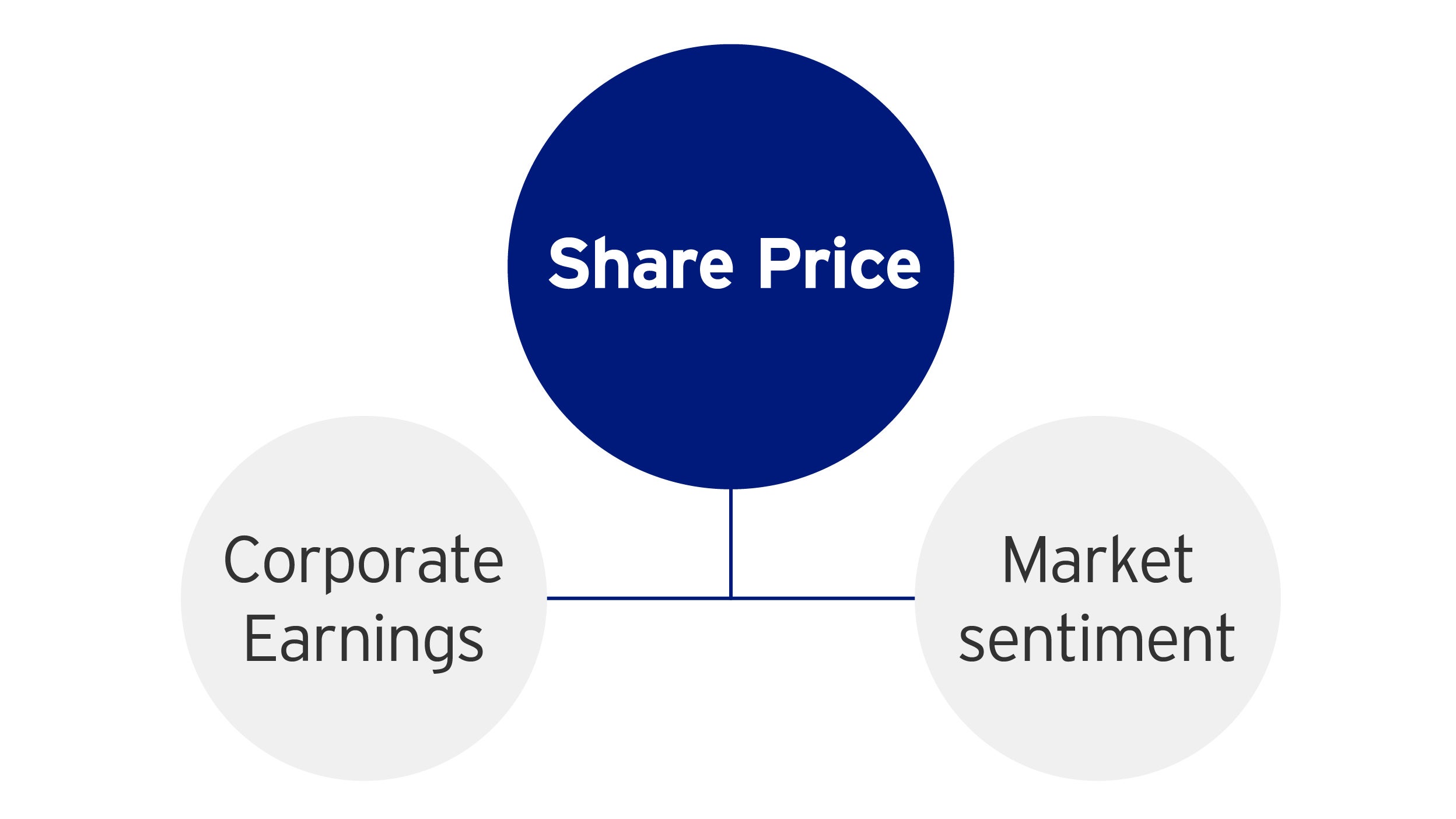
Why do share prices go up and down?
- If more people buy a stock (demand) than sell it (supply) => price moves up and vice versa.
- Factors that affect stocks prices (supply / demand) include corporate earnings and market sentiment.
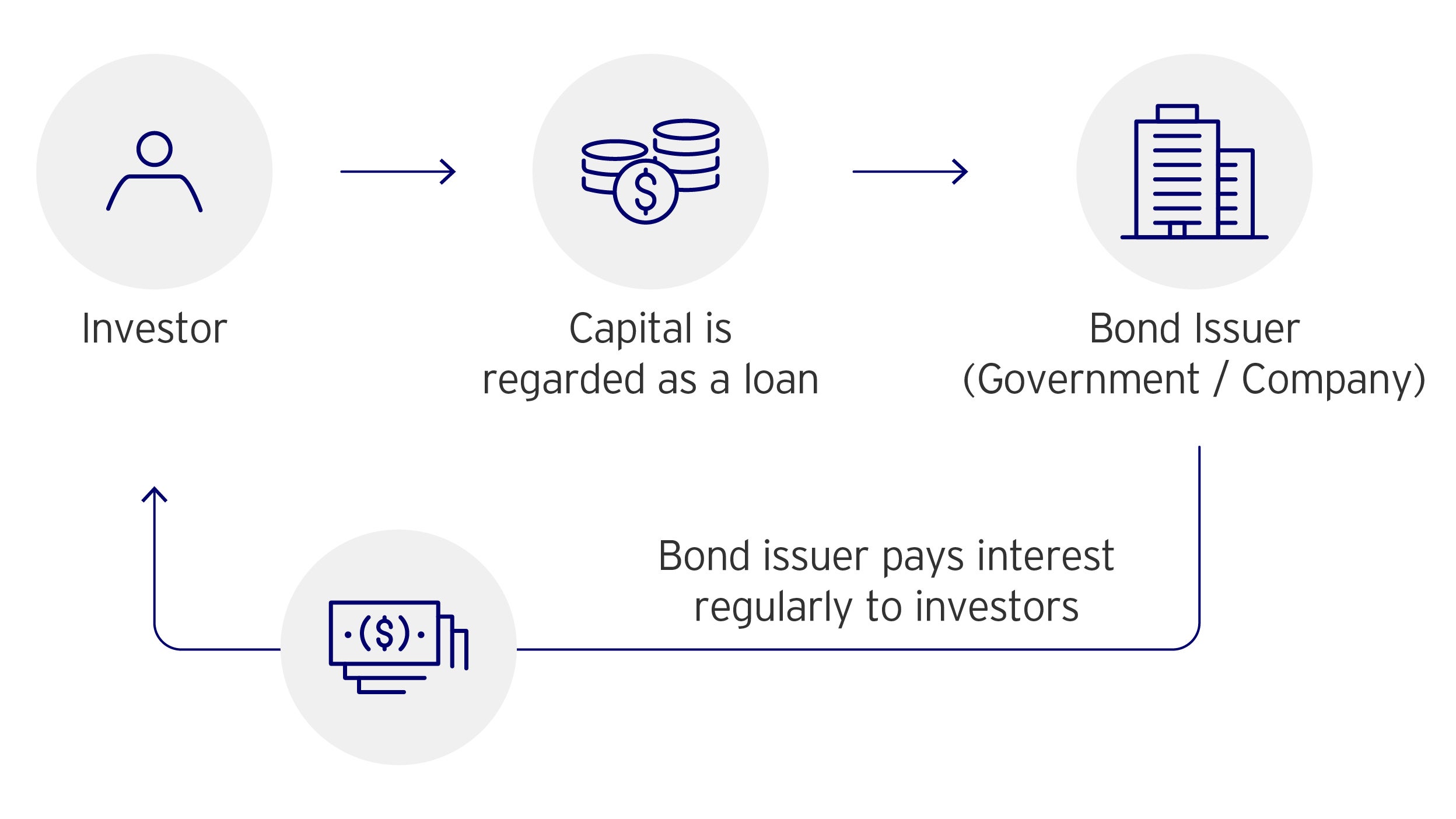
Bonds
- When a company / government issues a bond, it has agreed to repay capital plus interest on set dates.
- A bond investor, in effect, has lent money to the issuer.
- Some bond investors aim at earning a regular income. Others may try to profit by trading them.
For illustrative purpose only.
Why do bond prices go up and down?
| Factors | How does it impact bond prices? |
|---|---|
| Interest rates | When interest rates go down, bonds become more attractive - bond price rises and vice versa. |
| Market conditions | When market is risk-off, investors typically move to bonds from equities. Bond price could go up. |
| Credit Ratings | Bonds are assigned credit ratings by ratings agencies, such as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s. The ratings signal the agency’s view of the issuer’s ability to pay interest and principal. If a bond’s credit rating is downgraded, the bond price will likely fall. |
Mutual Funds
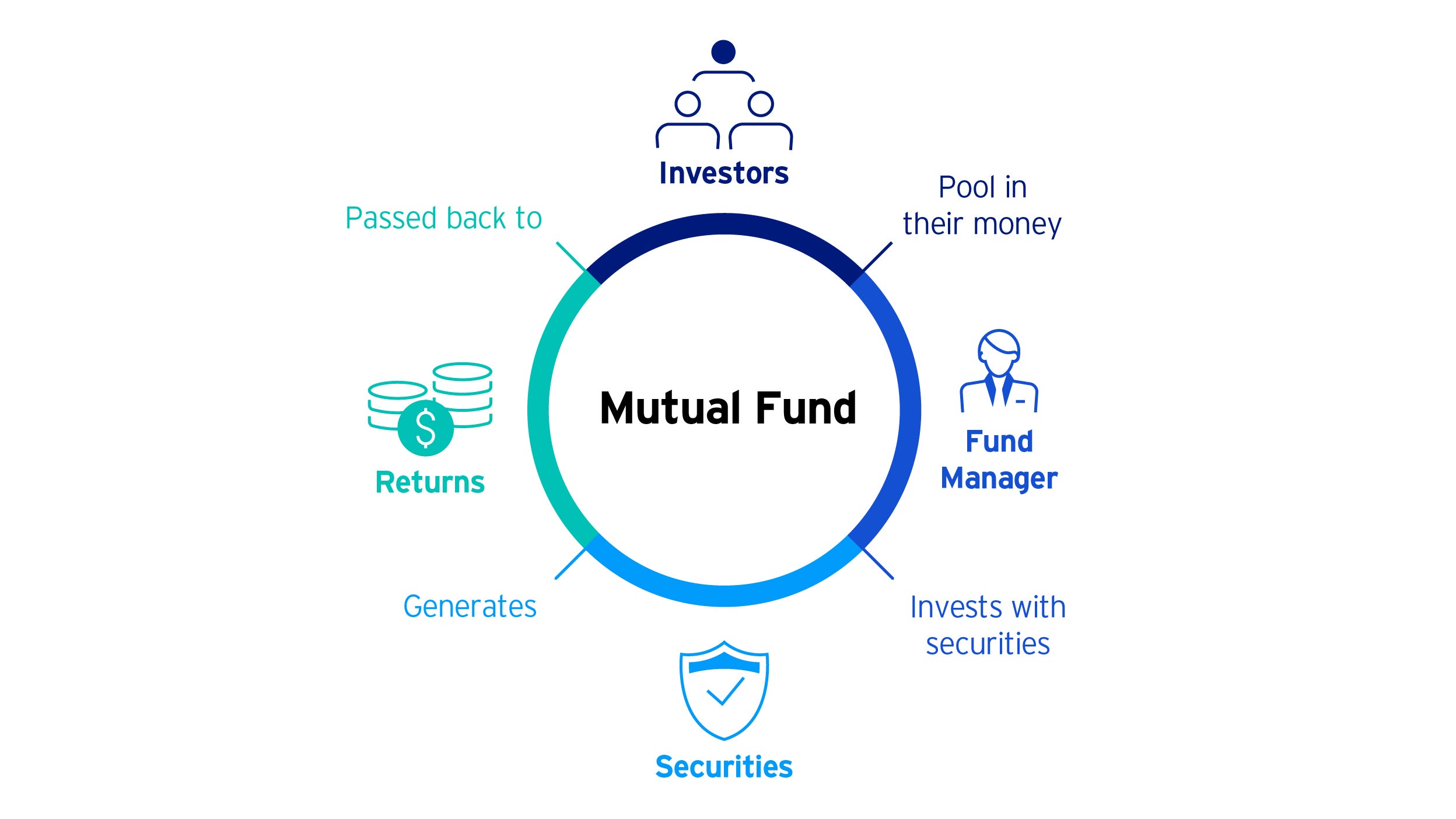
What are Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds pool money from investors to make investments into stocks, bonds or other assets in one portfolio. A fund manager chooses the underlying investments.
Different types of Mutual Fund?
| Mutual Fund | Underlying investments | Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Equity Fund | Invests in a basket of stocks. | Normally for long-term capital growth. |
| Bond Fund | Invests in debt securities normally issued by governments or corporations. | Normally for income. |
| Balanced/Multi-asset Fund | Invests in a mix of stocks, bonds, and/or money market instruments. | Normally a mixture of safety, income, and modest capital appreciation. |
| Money Market Fund (MMF) | MMF is a fund that invests in cash and short-term debt securities. It is considered one of the least risky investments, generating income and highly liquid. | Normally used by investors to manage cash or short-term savings. |
| Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) | Invests in a basket of securities — such as stocks, bonds and commodities — that often tracks an underlying index. | Normally to track the performance of a specific index. |
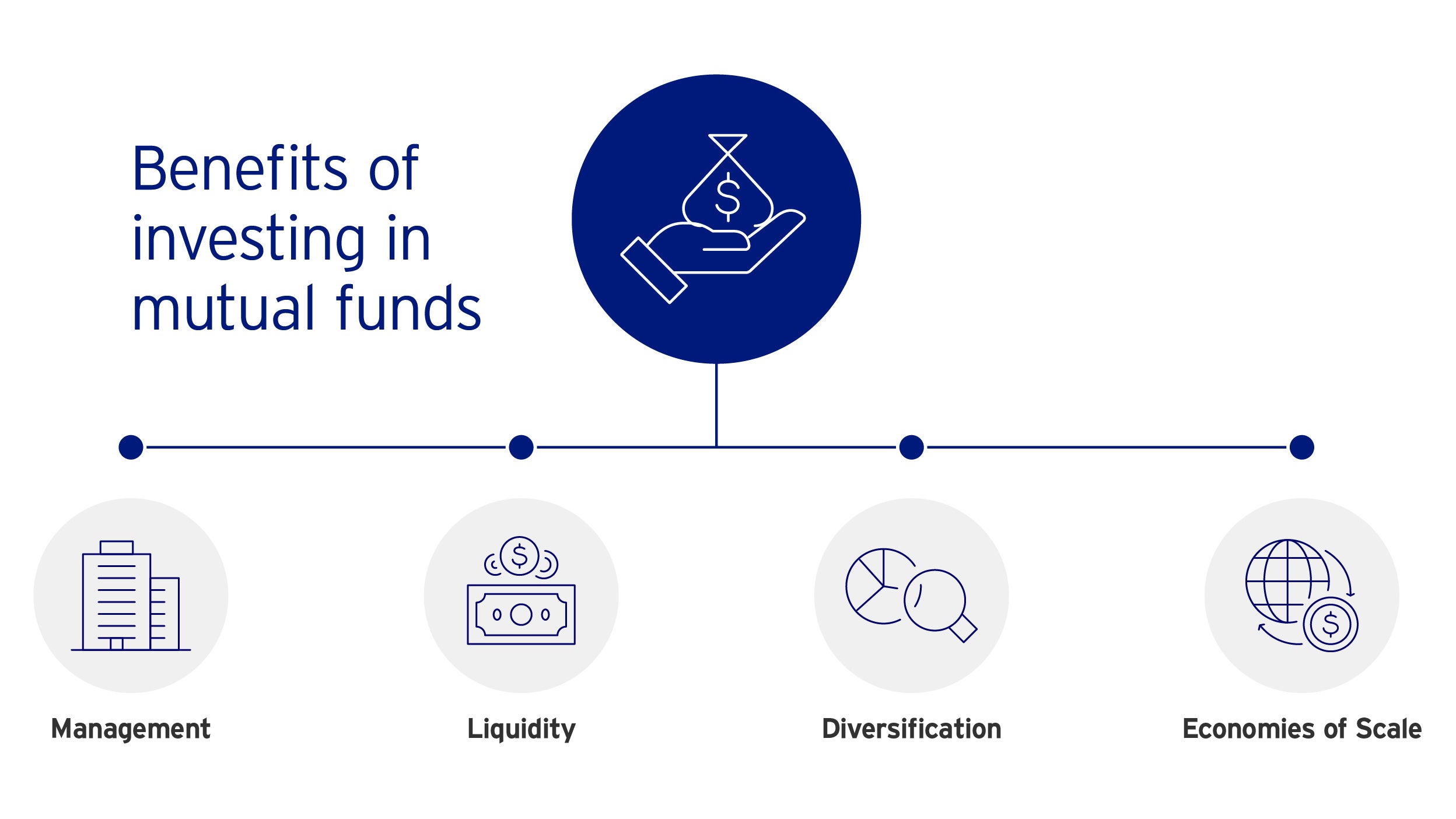
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds
| Benefits | |
|---|---|
| Management | Professional management teams often involving fund managers and research analysts. It should be noted that mutual funds charge management fees to cover their operating costs. |
| Liquidity | Funds are more liquid because they tend to be less volatile compared with a single security. |
| Diversification | Offer diversification or access to a wider variety of investments than an individual investor could afford to buy. |
| Economies of Scale | Mutual funds take advantage of their buying and selling volume to reduce transaction costs for their investors. When you buy a mutual fund (comprising 20 – 50 securities), you diversify without paying the 20 to 50 transaction fees that would give you a similarly diverse individual portfolio. |
Investment involves risk. Please review all financial material carefully before investing. The value of mutual funds can be volatile and could go down substantially.



