ESG Midyear Outlook for Investors: Positioning for long-term returns

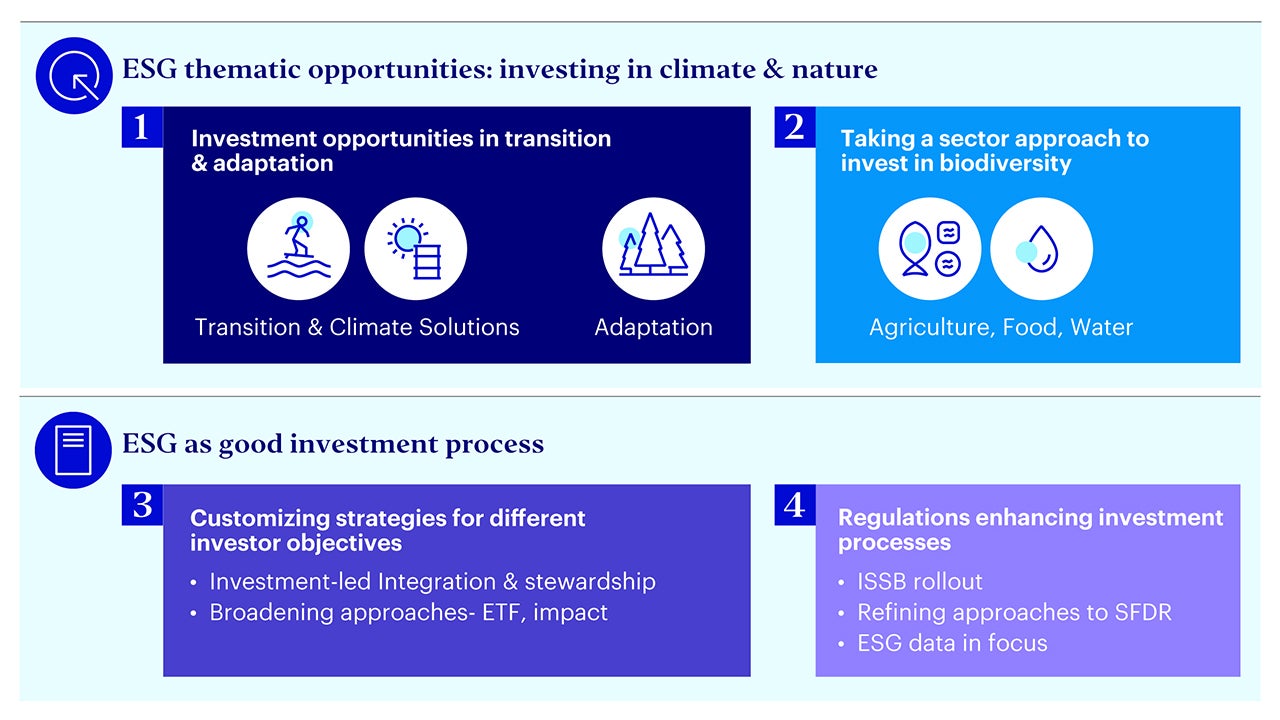
While markets have experienced divergence and uncertainty in the first half of 2023, environmental, social and governance, or ESG-oriented investing has continued to evolve. Top takeaways for investors interested in positioning their portfolios for long-term ESG-related return opportunities include:
- Investment opportunities in transition & adaptation as transition plans are implemented and efforts to establish climate resilience increase
- Taking a sector approach to invest in biodiversity such as on agrifood & water
- Customizing strategies for different investor objectives through investment-led processes, ETFs and impact investing opportunities
- Regulations enhancing investment processes as the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) and regulations on ESG data could enhance baseline of sustainability disclosures allowing investors to make more informed decisions
Source: Invesco, for illustrative purposes only.
Thematic Opportunities: How can investors be investing for climate and nature?
1] Investment opportunities in transition & adaptation
Source: Bernstein Putting a price on carbon; Energy Tracker; IPCC WGIII AR6; IEA; UNEP Adaptation Gap Report (Adaptation Gap Report 2022 | UNEP - UN Environment Programme); Past performance is not a guarantee of future results.
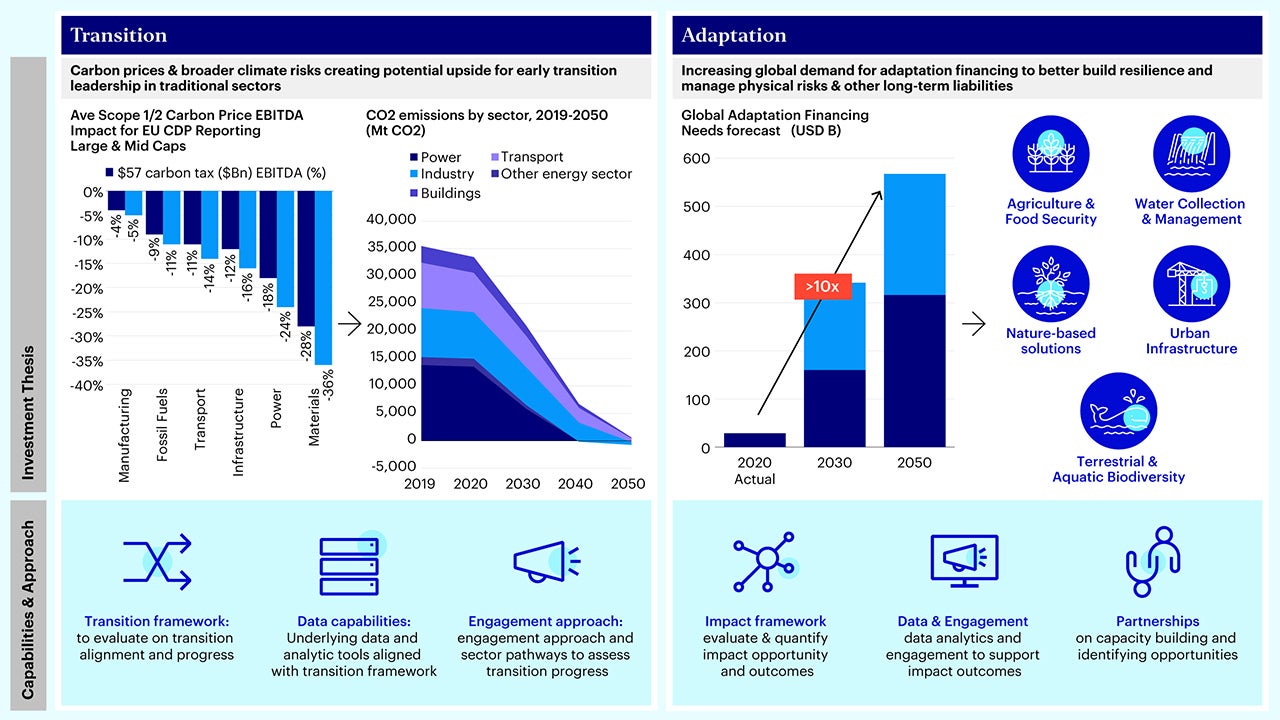
Transition: 2022 saw increasing number of investors focusing on transition driven by regulatory developments (FCA SDR “Improvers” Label1, launch of UK Transition Plan Taskforce2, G20 Transition Framework3) alongside a macroeconomic shift to quality and value. Challenges relating to defining transition, credible transition plans, and reliability of data remain. The underlying investment thesis is twofold:
- High-emitting sectors demonstrating transition leadership can capture potential valuation upside with the pricing in of carbon and productivity gains from green technology while also creating multiplier effects on downstream sectors that can benefit from upstream’ s technology adoption. This can be assessed by forward looking assessments on progress and plans. Invesco’s partnership with Tsinghua University Centre for Green Finance Research provides an investment framework for analyzing transition through disclosures, emissions analysis, industry pathways and green revenues.
- Return opportunities exist in climate solutions and technologies that benefit from broader adoption and scaling up due to decarbonization of high-emitting sectors.
Adaptation: Adaptation is front-and-center, driven by COP27’s launch of its Adaptation Agenda4 and the anticipation of El Nino in 20235. though financing gaps remain6 and greater standardization is required. The investment thesis centers on anticipation of an uptick in adaptation financing demand as more governments and corporates invest in projects to increase resilience to better manage physical risks in the longer-term.
2] Taking a sector approach to invest in biodiversity
- Attention to nature grew with global developments such as the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) releases of draft standards7 and Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. Existing challenges exist in having aggregable metrics and that biodiversity is highly localized and context specific. Investors’ ability to take a sector-based thematic approach is key. We see specific opportunities in:
- Agriculture and Food: Agriculture’s high dependency on nature and increasing risks in food security provide investment opportunities from precision agriculture to alternative protein. Invesco has conducted industry investment research with Farm Animal Investment Risk and Return (FAIRR) on investing in agrifood sectors and on protein producer data.
- Water: Investment opportunities across water supply chain arise from this broader thematic relating to both clean water availability and blue economy impact such as on fishing industries and aquatic biodiversity. Specific opportunities include water infrastructure like drainage systems, water treatment & sanitation, water equipment (like pumps).
Investment process: How can information about ESG factors enhance investment processes?
3] Customizing strategies for different investor objectives
- Investment-led process: 2022 saw global discourse on the role of ESG-related elements in investing. Correspondingly, approaches to considering financially material ESG factors or risks have evolved to enhance investment processes for generating long-term returns. Drivers of return may come from using ESG factors to quantify material financial risks and opportunities. Stewardship and active ownership may be tools for issuer dialogue on ESG factors affecting shareholder returns.
- Broadening approaches: The expanding range of ESG investing strategies can cater to increasing breadth of investor objectives:
- ESG ETFs: Global ESG ETFs have been gaining share of overall ETF AUM across regions8 providing increased choice for meeting diverse ESG and other investment preferences (such as additional weighting or on tracking error) of investors.
- Impact investing: Growth in interest in impact investing9 segment is driven by institutional investors and next-generation High Net Worth individual investors seeking deeper ESG outcomes.
4] Regulations enhancing investment processes
Regulations are evolving quickly. no longer just a checklist but on how it helps deepens investors’ approaches and processes for sustainable investing:
- International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) Rollout: All eyes are on finalized standards10 that are targeted to take effect in 2024 and adoption by different exchanges and regulators. Regions like Japan11 and Hong Kong12 have publicly announced plans on proposed adoption.
- Refining approaches to SFDR: Investors are moving beyond looking at labels or classifications to assessing investment managers’ process strength. Whether it’s on “sustainable investments” or in deciding between “Article 8 vs Article 9”, the underlying process of how an investor meets requirements and discloses relevant information becomes more important with more investors expected to ask deeper questions.
- Use of ESG data: We observe increasing regulatory momentum on guidance for ESG ratings and data providers (across UK, Japan, India, Singapore)
Looking Ahead: Focus on positioning
As markets face short-term uncertainty and pressure, the current market environment provides investors with an opportunity to consider their longer-term positioning. Sustainable investing offers both thematic opportunities and quality of process for investors to be best positioned for value creation and risk management.
Investment risks
The value of investments and any income will fluctuate (this may partly be the result of exchange rate fluctuations) and investors may not get back the full amount invested.
Footnotes:
-
1
FCA SDR Consultation CP22/20: Sustainability Disclosure Requirements (SDR) and investment labels (fca.org.uk)
-
2
HM Treasury Transition Plan Taskforce Transition Plan Taskforce | Setting a robust standard (transitiontaskforce.net)
-
3
G20 Transition Finance g20sfwg.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/2022-G20-Sustainable-Finance-Report-2.pdf
-
4
UNFCCC COP27 Presidency launches Adaptation Agenda to build climate resilience for 4 billion by 2030 - Climate Champions (unfccc.int)
-
5
BBC The high cost of an El Niño in 2023 - BBC Future
-
6
Climate Policy Initiative https://www.climatepolicyinitiative.org/publication/global-landscape-of-climate-finance-2021/
-
7
TNFD TNFD final draft proposes a 'Scopes' approach for nature - ESG Clarity
-
8
ESG Clarity ESG ETF assets will once again double in 2022 - ESG Clarity
-
9
Invesco Analysis https://www.invesco.com/apac/en/institutional/insights/esg/esg-and-impact-investing-in-asia.html
-
10
Thomson Reuters Global Baseline of Climate and Sustainability Disclosure Rules to Take Effect Next Year (thomsonreuters.com)
-
11
ESGInvestor Japan Sets ISSB Timeline – ESG Investor
-
12
HKEX Exchange Publishes Consultation Paper on Enhancement of Climate Disclosure under its ESG Framework (hkex.com.hk)




