China’s healthcare growth story outshines global peers

From vaccine development to innovative drugs and biotechnology, China’s healthcare companies have been growing strongly, outpacing some of the world’s leading industry players. We explore why one of China’s most diverse and expansive sector, its healthcare industry, is emerging as a growth opportunity.
China’s healthcare market is huge and diverse
Over the last decade, China’s healthcare industry has grown into a RMB 6.8 trillion market capitalization industry and is one of the largest sectors in the A share market. The sector has been growing at a compound annual growth rate of 15-20% (2015-2018), comprising of more than 370+ listed healthcare companies in China and Hong Kong.1 There are a multitude of factors driving the expansion of the industry (see Figure 1) including a 1.4 billion Chinese population that is aging with wealth to spend on quality healthcare products (see Figure 2).
Figure 1: Favorable factors supporting China’s healthcare sector
| Factors | Reasons |
| Large population that is aging | - Healthcare spending in China (2010-2018) grew faster than GDP - More elderly than children by 2049 |
| Affluent middle-class with spending power | - The Chinese middle-class is the largest in the world looking to spend on high quality health care products and services - Advanced in Chinese electronic technology help produce better quality medical devices |
| Advanced technology | - Healthcare value chain to shift towards innovative drugs with increased research and development (R&D) focus - Globalization drives multinational corporation (MNCs) to actively target Chinese market for next generation biologics, creates opportunities for China contract research organization (CRO) / contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) |
| Healthcare reforms | - Ongoing healthcare reforms show regulatory policies support the industry’s development - The drug price cuts on innovative drugs in 2020 were lower than expected - China National Medical Products Administration (equivalent to US FDA) helps accelerate drug review system and drive industry-wide enhancement of drug quality and innovation |
| Improved access to capital | - HKEX listing rule change for pre-revenue biotech - China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) fast-track approval for high-tech unicorns - Growing Private Equity/Venture Capital investments |
Source: Invesco as of 30 September 2020. For illustrative purposes only.
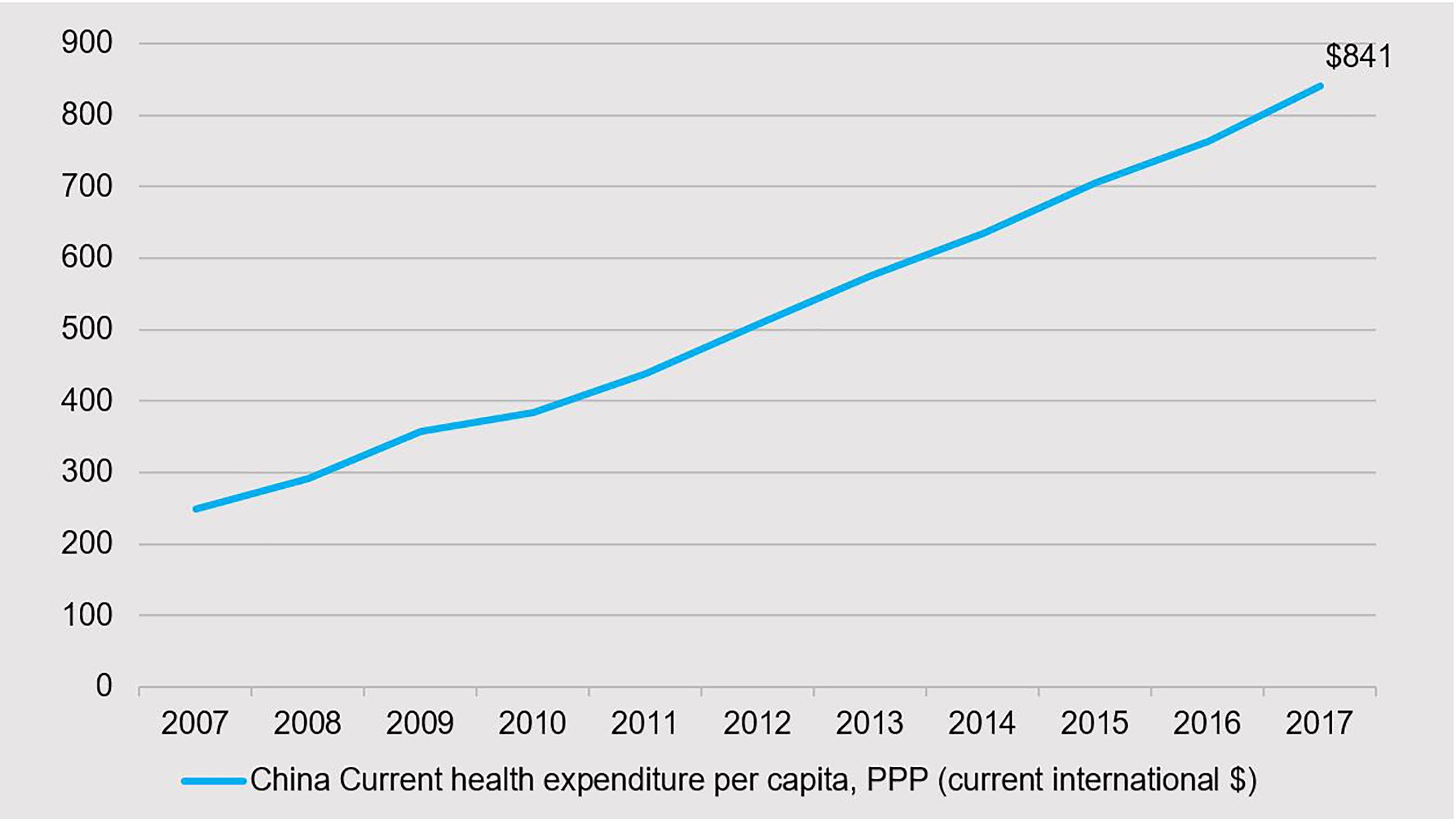
Outranking global peers with ample growth potential
Compared with global peers, Chinese healthcare companies have ample growth potential to expand market size (China’s top 20 domestic healthcare companies have market capitalizations of less than US$50 billion) and less expenditure on research and development (R&D) as a percentage of sales (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Ample Growth Potential for China Health Care Companies
| Top 20 Chinese domestic companies | Top 20 Multinationals (MNCs) | |
| Market capitalization | Less than < US$50 billion | From US$ 50 billion to US$400 billion |
| R&D as % of sales | ~11% of sales | ~20% of sales |
Source: Goldman Sachs, Bloomberg, PharmExec. as of 28 February 2021.
Within China’s A share market, there is a wide pool of subsectors for investors to choose from — each with its own unique supply and demand dynamics and business model. The growth profiles of a China healthcare stock versus a multinational healthcare company are very different. China healthcare stocks can broadly deliver double-digit revenue growth (see Figure 4) at 50 times forward PE (Price-to-Earnings) in contrast to US healthcare companies with low single digit earnings growth at 30 times forward PE.2
For growth-oriented investors, some Chinese healthcare companies have a strong pipeline of innovative drugs. China is the second largest prescription drug market in the world (US$140 billion market capitalization) after the States (US$393 billion) and expected to expand with more drugs to be included in the National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL).3
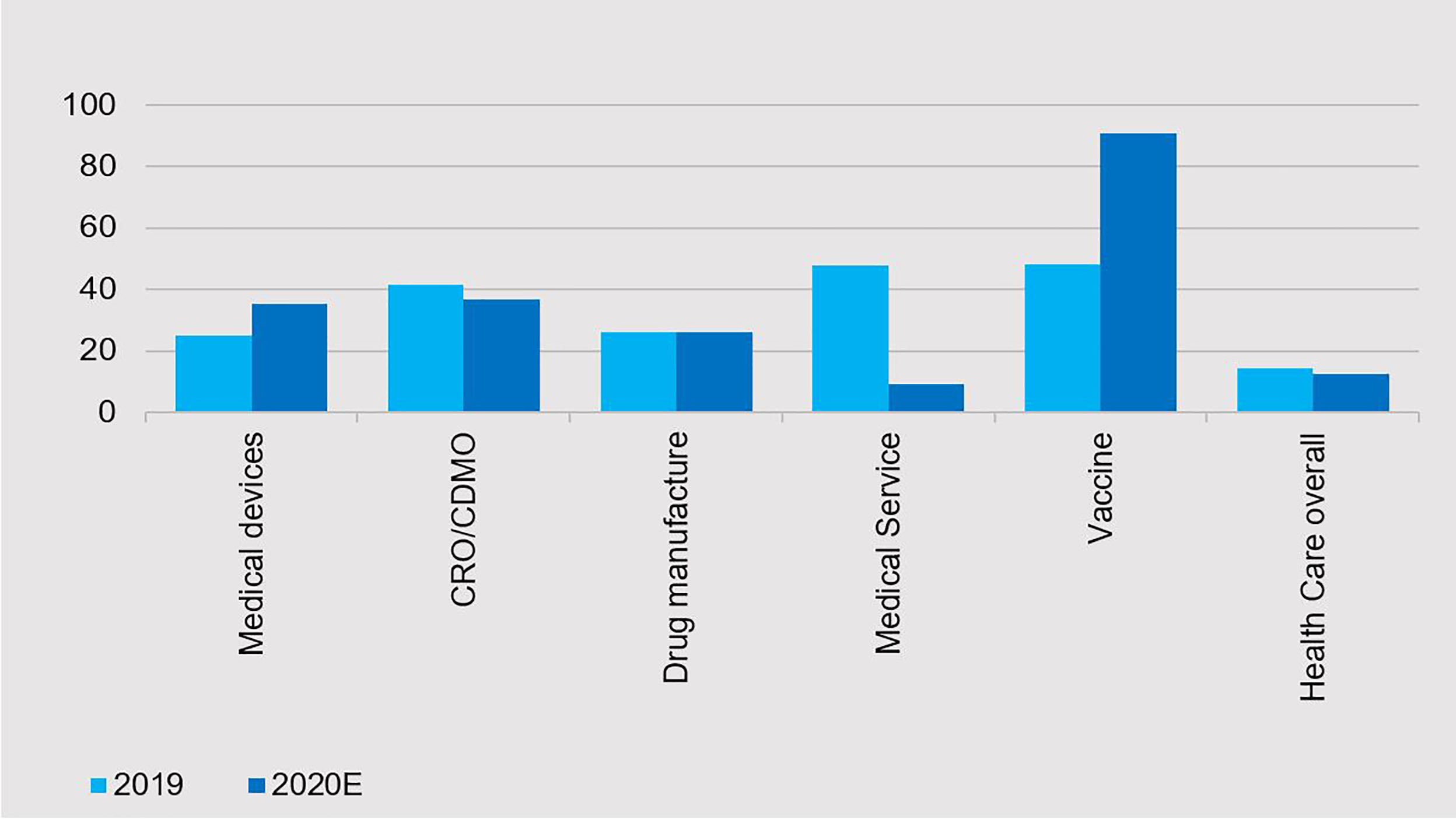
Unique opportunities in China’s healthcare sector
We focus on Chinese healthcare companies with long-term growth potential based on industry leadership and competitive advantages, clear business strategies and transparent corporate governance (see Figure 5).
Figure 5: Key growth subsectors in China
| Subsectors | Growth drivers |
| Medical devices | - Strong demand both overseas and domestic - Leverage on technological advances - Less policy risks on pricing - Has domestic capabilities which are competitive on costs, quality, and innovation |
| Innovative drug manufacturers | - Prefer drug makers with strong pipelines of innovative drugs over generic drug manufacturers - Favor competitive large-cap pharma companies with strong pipeline and mid-cap biotech companies with unique characteristics |
| Contract research organization (CRO) and Contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) | - Strong outsourcing demand from global and domestic drug companies upgrading their products through increased R&D |
| Vaccine manufacturers | - Supported by a low penetration rate - Rising market share domestically - Contribution of revenues from COVID-19 vaccines and new products |
Source: Invesco as of 30 December 2020. For illustrative purposes only.
We remain positive on the China healthcare sector and A share market in 2021. Having efficiently contained the pandemic, we expect a strong economic recovery in China as well as foreign and domestic fund inflows stemming from wealth management products of banks into equity funds. With its advances in technological research and development, China’s healthcare industry has come a long way in the last decade, bettering the lives of its population and providing greater opportunities for investors.
Investment risks
The value of investments and any income will fluctuate (this may partly be the result of exchange rate fluctuations) and investors may not get back the full amount invested.
When investing in less developed countries, you should be prepared to accept significantly large fluctuations in value.
Investment in certain securities listed in China can involve significant regulatory constraints that may affect liquidity and/or investment performance.
^1 Invesco, Goldman Sachs research; as of September 30, 2020.
^2 Invesco Great Wall IGW, Bloomberg data for MSCI CHINA A Onshore HealthCare index as of 7 January 2021. Bloomberg data for MSCI USA index, GICS sector: Healthcare as of 5 January 2021.
^3 Beigene company reports. PwC Report on Global Pharmaceutical Trend, IMS Health data, McKinsey Industry Report. J.P. Morgan, Private and public measures to improve health care – 2020 Outlook, February 2020.




